Enterprise Cloud Migration Unlocking New Possibilities
Enterprise Cloud Migration sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As organizations strive to remain competitive in an ever-evolving digital landscape, the shift to cloud-based solutions is not just an option but a necessity. Understanding the nuances of cloud migration, including its benefits, challenges, and processes, is crucial for any enterprise looking to enhance efficiency, scalability, and security.
This comprehensive guide delves deep into the multiple facets of enterprise cloud migration, exploring various cloud models such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, while also highlighting the essential steps in the migration process, the tools available, security considerations, cost management strategies, and post-migration practices that can lead to sustained success.
Overview of Enterprise Cloud Migration
Enterprise cloud migration refers to the process of transferring an organization’s data, applications, and other business elements from on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based services. This transition is significant as it allows companies to leverage advanced technologies, enhance operational efficiency, and respond more flexibly to market demands. With the increasing need for scalability and agility in business operations, cloud migration has become a pivotal strategy for organizations aiming to remain competitive in a digital landscape.Migrating to the cloud offers a myriad of benefits for organizations, including cost savings, enhanced collaboration, and improved security.
By utilizing cloud services, businesses can significantly reduce the expenses associated with maintaining physical infrastructure. Furthermore, cloud platforms provide a collaborative environment where teams can work simultaneously from different locations, fostering innovation and productivity. The cloud also generally provides improved security features, protecting sensitive data from breaches with advanced encryption methods and continuous monitoring.
Benefits of Cloud Migration
Cloud migration provides several advantages that can positively impact an organization’s performance and bottom line. These benefits include:
- Cost Efficiency: Migrating to the cloud reduces the need for significant upfront capital expenditures on hardware and maintenance. Organizations typically adopt a pay-as-you-go model, which can lead to considerable savings.
- Scalability: Businesses can easily scale resources up or down based on demand, enabling them to respond swiftly to changes in the market or operational needs.
- Enhanced Performance: Cloud providers often deliver superior infrastructure and server capabilities compared to traditional setups, resulting in faster application performance and improved user experience.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud solutions often include built-in data backup and disaster recovery options, ensuring business continuity in case of unexpected disruptions.
- Security Features: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures and compliance standards, offering organizations advanced protections that might be cost-prohibitive to implement independently.
Challenges of Cloud Migration
While the benefits of cloud migration are substantial, organizations often encounter several challenges during the migration process. Understanding these hurdles is critical for successful implementation and includes the following points:
- Data Security and Compliance: Ensuring data remains secure and compliant with regulations during and after migration can be complex, particularly in industries with stringent data protection laws.
- Legacy System Integration: Integrating existing legacy systems with cloud services can present significant technical difficulties, often requiring substantial resources and expertise.
- Downtime and Business Disruption: The migration process can lead to temporary downtime, impacting business operations and customer experience if not managed carefully.
- Cost Overruns: While cloud migration can reduce costs in the long run, organizations may face unexpected expenditures during the transition period, particularly if thorough planning is lacking.
- Change Management: Employees may resist transitioning to new systems and processes, necessitating effective change management strategies to facilitate a smooth transition.
“The cloud is about how you do computing, not where you do computing.” – Paul Maritz
Different Models of Cloud Migration
The shift to cloud environments has led to the emergence of various migration models, each tailored to meet different business needs. Understanding these models helps organizations select the right approach that aligns with their strategic objectives and operational requirements. This section explores the primary cloud migration models—Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS)—along with their advantages, disadvantages, and real-world examples of successful adoption.
IaaS Overview
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. This model allows businesses to rent IT infrastructure, such as servers, storage, and networking, rather than investing in physical hardware. IaaS is highly flexible and scalable, making it an attractive option for organizations looking to minimize capital expenditures while maintaining control over their infrastructure.
- Advantages of IaaS:
- Cost efficiency due to pay-as-you-go pricing models.
- Scalability allows businesses to rapidly adjust resources based on demand.
- High level of control over infrastructure and applications.
- Disadvantages of IaaS:
- Management complexity as organizations need to handle their own software updates and security.
- Potential for higher costs if resources are not managed effectively.
- Requires skilled IT personnel to manage infrastructure effectively.
- Examples:
- Dropbox utilizes IaaS for data storage and processing.
- Netflix leverages IaaS through Amazon Web Services for its video streaming services, allowing it to handle millions of concurrent users.
PaaS Overview
Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a platform allowing developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without the complexity of managing underlying infrastructure. This model typically includes operating systems, development tools, and database management systems, streamlining the development process.
- Advantages of PaaS:
- Accelerates the development process with built-in software components and tools.
- Reduces operational overhead as the provider manages infrastructure and middleware.
- Facilitates collaboration among distributed teams with integrated development environments.
- Disadvantages of PaaS:
- Limited control over the underlying infrastructure may hinder customization.
- Dependency on the service provider for system updates and support.
- Potential for vendor lock-in, making it difficult to change providers.
- Examples:
- Google App Engine provides a robust platform for developing and hosting web applications.
- Heroku is favored by startups for its simplicity in deploying applications in multiple languages.
SaaS Overview
Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for installations and maintenance. This model is ideal for organizations seeking to provide end-users with easy access to software without the complexities of managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Advantages of SaaS:
- Accessibility from any device with an internet connection increases productivity.
- Automatic updates ensure that users always have the latest features.
- Lower initial costs and predictable monthly expenses as it often operates on a subscription model.
- Disadvantages of SaaS:
- Limited customization options may not meet specific business needs.
- Data security concerns as sensitive information is stored off-premises.
- Dependence on internet connectivity for software access.
- Examples:
- Salesforce is a leading customer relationship management tool used by businesses globally.
- Microsoft 365 provides a suite of office applications accessible from anywhere, enhancing collaboration among teams.
Steps in the Cloud Migration Process

Source: codemotion.com
The process of migrating to the cloud is a multifaceted journey that requires careful planning and execution. Understanding the key phases involved in this migration not only streamlines the transition but also maximizes the benefits of cloud technology. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the steps involved in migrating to the cloud.The cloud migration process can be divided into several key phases, starting from initial assessment and planning to eventual execution and optimization.
Each phase is crucial to ensure a smooth transition, minimize risks, and achieve the desired outcomes.
Key Phases in the Cloud Migration Process
The cloud migration journey is typically broken down into five essential phases:
1. Assessment and Planning
This phase involves evaluating the current IT landscape, understanding business requirements, and developing a migration strategy. Organizations should assess their existing applications, data, and infrastructure to identify what is suitable for migration.
2. Design
In this phase, the organization Artikels the architecture of the future cloud environment. This includes selecting the appropriate cloud model (public, private, or hybrid), defining security protocols, and determining compliance requirements.
3. Migration
This is the execution phase where data and applications are actually moved to the cloud. It involves using migration tools and techniques to transfer workloads, ensuring minimal downtime and data integrity.
4. Validation and Testing
Post-migration, it’s crucial to validate that everything has been transferred correctly. This phase involves testing applications and systems to ensure they are functioning as expected in the new environment.
5. Optimization and Monitoring
Once the migration is complete, organizations should continuously monitor the cloud environment for performance, efficiency, and security. This phase also includes optimizing resource usage to ensure cost-effectiveness.
Checklist for Cloud Migration
A detailed checklist is essential for organizations to follow during migration. It ensures that all critical aspects are covered and helps avoid common pitfalls. – Pre-Migration
Identify stakeholders and form a migration team.
Analyze current IT infrastructure and applications.
Define objectives and success metrics for the migration.
Select a suitable cloud provider and model.
- Create a risk management plan.
- During Migration
Execute the migration plan step-by-step.
Monitor data transfer and application performance.
Ensure data security and compliance throughout the process.
- Communicate regularly with stakeholders about progress.
- Post-Migration
Validate that all applications and data function correctly.
Conduct performance testing to optimize cloud resources.
Review migration outcomes against success metrics.
Train staff on new cloud systems and processes.
Timeline and Expected Outcomes for Each Phase
A well-structured timeline is essential for effective cloud migration. Below is a table outlining the typical duration and expected outcomes for each phase of migration.
| Phase | Duration | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Assessment and Planning | 2-4 weeks | Complete understanding of current landscape and a solid migration roadmap. |
| Design | 2-3 weeks | Defined architecture for cloud environment tailored to business needs. |
| Migration | 3-6 weeks | Successful transfer of applications and data with minimal downtime. |
| Validation and Testing | 1-2 weeks | Ensured functionality of applications and data integrity in the cloud. |
| Optimization and Monitoring | Ongoing | Continuous improvement in performance, efficiency, and resource utilization. |
“Successful cloud migration requires meticulous planning and execution at each phase to fully leverage the benefits of cloud technology.”
Tools and Technologies for Cloud Migration
Cloud migration involves moving data, applications, and workloads from on-premises infrastructure to cloud environments. To facilitate this process, various tools and technologies have emerged, designed to streamline and optimize the migration experience while ensuring data integrity and security. Choosing the appropriate tools is crucial for a successful transition to the cloud.
Leading Tools for Cloud Migration
A variety of tools are available to aid organizations in their cloud migration efforts. Here are some of the most notable ones that have proven effective:
- AWS Migration Hub: This service provides a central location for tracking the progress of application migrations across multiple AWS and partner solutions, helping organizations streamline their migration processes.
- Azure Migrate: A comprehensive hub for tools to start, execute, and track migrations to Azure. It supports various migration scenarios, making it adaptable for different organization sizes.
- Google Cloud Migrate: Specifically designed for migrating virtual machines from on-premises or other cloud platforms directly to Google Cloud, ensuring a seamless transition with minimal downtime.
- CloudEndure: This tool allows for continuous data replication, enabling quick recovery in case of failure and simplifying the migration process significantly. It works with multiple cloud environments.
- VMware Cloud on AWS: This service extends VMware’s software-defined data center (SDDC) to the AWS Cloud, allowing organizations to run VMware workloads on AWS infrastructure without modification.
The selection of these tools depends on various factors, including organization size, existing infrastructure, and specific migration needs.
Criteria for Selecting Migration Tools, Enterprise Cloud Migration
Choosing the right migration tools requires careful consideration of several criteria to align them with an organization’s specific requirements. Here are the essential factors to consider:
- Compatibility: Ensure the tool supports existing systems and applications to avoid any compatibility issues during migration.
- Scalability: Opt for tools that can handle current data sizes while also being able to scale for future growth as the organization expands.
- User-Friendliness: Tools should offer intuitive interfaces and usability to reduce the learning curve and facilitate team adoption.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including licensing, implementation, and operational costs, to choose a financially viable solution.
- Support and Community: Adequate support services and an active community can significantly ease the troubleshooting process and provide additional resources.
Considering these criteria can greatly enhance the likelihood of a successful migration.
Case Studies of Successful Migrations
Real-world examples highlight how specific migration tools have facilitated successful transitions to the cloud. Here are a few illustrative case studies:
- Netflix: Utilizing AWS tools, Netflix successfully migrated their entire infrastructure to the cloud, achieving flexibility and scalability while enhancing their service availability to millions of users globally.
- GE Aviation: By employing Azure Migrate, GE Aviation transferred a substantial amount of their workloads to Azure, which resulted in improved operational efficiency and reduced costs associated with maintaining on-premises data centers.
- Dow Chemical: Dow used CloudEndure to migrate their applications with minimal downtime, allowing them to maintain business continuity and operational integrity throughout the migration process.
- Snap Inc.: Using Google Cloud Migrate, Snap leveraged the cloud’s capabilities to handle surges in usage, particularly during high-traffic events, ensuring seamless performance for their platform.
These case studies illustrate the effectiveness of well-chosen migration tools in achieving successful cloud transitions, ultimately driving business growth and efficiency.
Security Considerations in Cloud Migration
When organizations transition to the cloud, they face various security challenges that can impact the integrity and confidentiality of their data. Understanding these risks is essential for successful cloud migration. Failing to address security considerations can lead to data breaches, compliance violations, and loss of customer trust. The migration process must be approached with a comprehensive strategy that prioritizes security throughout every phase.The security risks associated with migrating to the cloud are multifaceted.
Potential threats include data breaches, unauthorized access, data loss, and compliance failures. Migrating sensitive data can expose organizations to cyberattacks if not handled securely. Additionally, the cloud environment can introduce vulnerabilities due to shared resources and multi-tenancy, where data from different customers resides on the same physical server. Protecting against these risks is crucial for maintaining data security and aligning with regulatory standards.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Security During the Migration Process
Implementing best practices can significantly enhance data security during cloud migration. Organizations should adopt a proactive approach to identify and mitigate risks associated with the migration process. Here are essential practices to consider:
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities before migration.
- Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to safeguard sensitive information.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to control access to cloud resources.
- Establish a robust data backup and recovery plan to prevent data loss.
- Regularly update and patch systems and applications to address security flaws.
- Monitor and audit cloud activities to detect any unauthorized access or anomalies.
Employing these practices helps ensure that sensitive data remains protected throughout the migration process and reduces the risk of security incidents.
Compliance Requirements to Adhere to During Migration
Organizations must also consider compliance requirements that govern data security during cloud migration. Adhering to these regulations is essential for avoiding legal repercussions and maintaining customer trust. Below is a list of common compliance requirements relevant to cloud migration:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Ensures the protection of personal data for individuals within the EU.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Governs the handling of protected health information (PHI) in the healthcare industry.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): Mandates security measures for organizations that handle credit card transactions.
- Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP): Establishes a standardized approach to security assessment for cloud services used by federal agencies.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): Requires accurate financial reporting and data integrity for publicly traded companies.
Understanding and adhering to these compliance requirements not only enhances security but also builds credibility with customers and stakeholders. Organizations should ensure that their cloud service providers are compliant with relevant regulations to mitigate risks effectively.
Cost Management in Cloud Migration
Estimating and managing costs effectively is a critical aspect of cloud migration that can significantly influence the success of the overall project. Organizations often face unexpected expenses during the transition from on-premises systems to the cloud, making it essential to have a clear understanding of potential costs and savings.Organizations can estimate costs associated with cloud migration by considering several key factors, including the resources needed, licensing fees, potential training costs, and ongoing operational expenses.
A well-structured approach to budgeting will help in tracking these costs and maintaining control over the migration process.
Estimating Costs for Cloud Migration
A comprehensive cost estimation involves analyzing both direct and indirect expenditures related to cloud migration. The following methods can help organizations achieve effective budgeting:
- Assessment of Current Infrastructure: Evaluate existing on-premises systems to identify hardware, software, and maintenance costs that can be eliminated or reduced post-migration.
- Cloud Provider Pricing Models: Research and compare pricing structures of different cloud providers, including pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and spot pricing, to find the most cost-effective solution.
- Third-Party Tools and Services: Consider using cost estimation tools from cloud providers or third-party vendors that provide detailed analysis based on organizational needs.
- Operational Costs: Factor in ongoing costs associated with cloud management, such as data transfer fees, storage costs, and support services.
Effective Budgeting and Cost Control
Implementing a robust budgeting strategy during cloud migration can help in maintaining financial discipline. Consider the following approaches:
- Define Clear Objectives: Establish specific migration goals and the expected outcomes, which will help in justifying expenditures.
- Regular Monitoring: Utilize monitoring tools to track resource consumption and expenses over time, allowing organizations to adjust budgets accordingly.
- Cost Allocation: Assign budgets to specific departments or projects to enhance accountability and visibility into cloud spending.
- Review and Adjust: Conduct regular reviews to assess spending against the budget and make necessary adjustments based on current usage and future projections.
Potential Cost Savings from Cloud Migration
Migrating to the cloud often results in significant cost savings compared to maintaining on-premises systems. The table below illustrates potential savings across various cost categories.
| Cost Category | On-Premises Cost | Cloud Cost | Potential Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Purchases | $200,000 | $50,000 | $150,000 |
| Software Licensing | $50,000 | $20,000 | $30,000 |
| Maintenance and Support | $30,000 | $10,000 | $20,000 |
| Energy Costs | $15,000 | $5,000 | $10,000 |
| Total | $295,000 | $85,000 | $210,000 |
The savings highlighted demonstrate the potential for organizations to not only reduce their operational costs but also reallocate resources more effectively to drive innovation and growth.
Post-Migration Strategies: Enterprise Cloud Migration
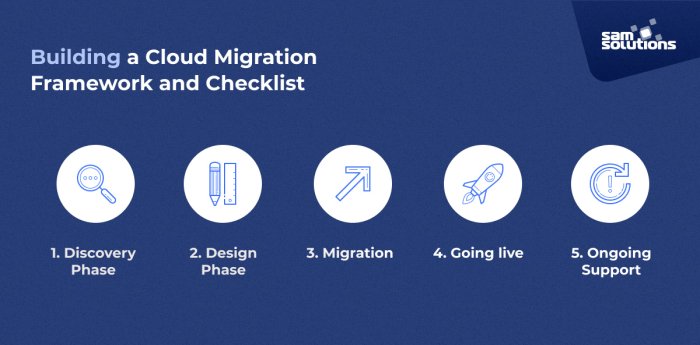
Source: sam-solutions.us
In the realm of cloud migration, the work doesn’t stop once the data is transferred and applications are running smoothly. Post-migration strategies play a crucial role in ensuring that organizations fully leverage their new cloud environment. These strategies focus on the evaluation of the migration process, continuous monitoring, performance optimization, and staff training to sustain long-term benefits.Post-migration evaluations are essential for organizations to assess the success of their migration efforts.
This phase involves analyzing various aspects of the migration to determine effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. Key focus areas include application performance, security posture, compliance with regulatory standards, and cost management.
Monitoring and Optimizing Cloud Performance
Following migration, organizations must implement robust monitoring practices to maintain optimal cloud performance. Regular assessments not only help in identifying potential issues but also offer insights into usage patterns and resource allocation.To effectively monitor and optimize cloud performance, organizations can adopt the following procedures:
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define relevant KPIs to measure application performance, such as response time, uptime, and resource utilization. Regularly review these metrics to gauge performance against expectations.
- Utilize Monitoring Tools: Invest in comprehensive monitoring solutions that provide real-time insights into cloud performance. Tools like AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or third-party services can track resource usage, application performance, and security alerts.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Schedule periodic audits to assess resource allocation and identify underutilized or over-provisioned resources. This process helps in optimizing costs and improving efficiency.
- Implement Automated Scaling: Leverage auto-scaling features to dynamically adjust resources based on the current demand. This ensures that applications remain responsive during peak usage times while controlling costs during low usage periods.
- Gather User Feedback: Regularly solicit feedback from users to identify pain points and improvement opportunities in application performance. This information can guide adjustments for enhanced user experience.
Training and Support for Staff
Effective training and support for staff is vital in a post-migration environment to ensure that teams are equipped to utilize the new cloud infrastructure effectively. Adequate training minimizes disruptions and enhances the overall productivity of the organization.Key strategies for implementing training and support include:
- Develop Comprehensive Training Programs: Create tailored training sessions that cover cloud services, tools, and best practices. For example, hands-on workshops or online courses can facilitate learning about specific cloud platforms.
- Establish a Support System: Set up a dedicated support team or help desk that staff can turn to for assistance with cloud-related issues. This team should be knowledgeable about the cloud environment and capable of providing timely support.
- Encourage Continuous Learning: Foster a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging staff to pursue certifications and ongoing education in cloud technologies. This not only enhances their skills but also keeps the organization up-to-date with the latest developments.
- Facilitate Knowledge Sharing: Promote collaboration and knowledge sharing among employees through regular meetings or forums. This encourages the exchange of tips, experiences, and best practices across the organization.
Overall, by focusing on post-migration evaluations, monitoring and optimizing cloud performance, and providing adequate training and support for staff, organizations can ensure that their cloud migration efforts yield long-term benefits and drive business success.
Final Thoughts

Source: cisco.com
In conclusion, transitioning to the cloud is a transformative journey that can propel enterprises toward unprecedented growth and innovation. By thoroughly understanding the migration process, leveraging the right tools, and prioritizing security and cost management, organizations can not only overcome the hurdles they face but also thrive in a cloud-driven environment. The future of business lies in the cloud, and taking that leap can unlock a realm of possibilities.
Essential FAQs
What is enterprise cloud migration?
Enterprise cloud migration refers to the process of transferring an organization’s data, applications, and services from on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based environments, aiming to enhance flexibility and scalability.
What are the main benefits of cloud migration?
Benefits include cost savings, improved collaboration, enhanced data security, scalability, and access to advanced technologies.
What challenges do organizations face during migration?
Common challenges include data security concerns, potential downtime, integration complexities, and managing change within the organization.
How can organizations estimate the costs associated with cloud migration?
Organizations can analyze current IT expenditures, assess migration tool costs, consider ongoing operational expenses, and evaluate potential cost savings from cloud adoption.
What role does training play in post-migration success?
Training is vital for ensuring staff can effectively utilize new cloud systems, maximizing productivity and minimizing frustration.

