Predictive Analytics Software Unleashing Data Potential
Predictive Analytics Software is revolutionizing how businesses approach decision-making by transforming vast amounts of data into actionable insights. This innovative technology has evolved significantly over the years, gaining traction across various industries such as finance, healthcare, and marketing. As today’s companies strive to stay competitive, understanding the capabilities and applications of predictive analytics is more crucial than ever.
From predicting customer behaviors to optimizing operational efficiency, predictive analytics tools provide organizations with the foresight needed to navigate complex environments. This overview delves into the features, techniques, implementation strategies, real-world applications, and future trends that shape this dynamic field.
Overview of Predictive Analytics Software
Predictive analytics software plays a crucial role in harnessing data to forecast future events and trends. By employing statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques, this software enables organizations to make informed decisions based on data-driven insights. The ability to anticipate changes in market conditions, consumer behavior, or operational performance empowers businesses to strategize effectively and enhance their competitive edge.The evolution of predictive analytics has been remarkable, transitioning from basic statistical methods to sophisticated machine learning algorithms.
In its early days, predictive analytics primarily involved simple linear regression and historical data analysis. However, advancements in technology have paved the way for more complex models that can analyze vast amounts of unstructured data. This evolution has had a profound impact across various industries, enhancing operational efficiency, risk management, and customer relationship strategies.
Industries Utilizing Predictive Analytics Software
Numerous industries benefit from the application of predictive analytics software, leveraging its capabilities to optimize performance and enhance decision-making. Below are some of the key sectors where predictive analytics is commonly employed:
- Healthcare: Predictive analytics assists in patient care by forecasting disease outbreaks, predicting patient admissions, and optimizing treatment plans based on historical data.
- Finance: In the financial sector, organizations use predictive models to assess credit risk, detect fraudulent transactions, and tailor investment strategies to market changes.
- Retail: Retailers employ predictive analytics to personalize marketing campaigns, manage inventory levels, and predict consumer purchasing behavior, ensuring better stock management and customer satisfaction.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing companies utilize predictive maintenance strategies, forecasting equipment failure to minimize downtime and optimize production schedules.
- Telecommunications: Predictive analytics helps telecom companies manage customer churn by identifying at-risk customers and implementing targeted retention strategies.
The ability to harness predictive analytics not only helps organizations in these industries to operate more effectively but also fosters innovation and drives growth. As data continues to proliferate, the relevance and necessity of predictive analytics will likely expand, underscoring its importance in the modern business landscape.
“Predictive analytics transforms data into actionable insights, enabling businesses to anticipate challenges and seize opportunities.”
Key Features of Predictive Analytics Software
Source: gmpis.com
Predictive analytics software is designed to help organizations make informed decisions by analyzing data and forecasting potential outcomes. These tools leverage statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to recognize patterns in data, enabling businesses to anticipate future trends and behaviors. Understanding the key features of predictive analytics software is essential for organizations looking to utilize these tools effectively.One of the most significant features of predictive analytics software is its ability to handle large volumes of data from various sources.
The software can process structured and unstructured data, allowing companies to gain a holistic view of their information landscape. Other vital features include automated data preparation, model building capabilities, and real-time analytics that provide immediate insights.
Essential Features of Predictive Analytics Software
The effectiveness of predictive analytics tools is determined by their essential features. Here are some critical functionalities that these tools provide:
- Data Integration: The ability to aggregate data from multiple sources, such as databases, CRM systems, and social media platforms, for a comprehensive analysis.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Incorporation of various machine learning models that can be used to analyze data and make predictions.
- Visualization Tools: Built-in dashboards and visualization options that facilitate easy interpretation of data through graphs, charts, and reports.
- Real-time Analytics: Capability to analyze data in real-time, enabling prompt decision-making and immediate response to changing conditions.
- Scalability: The software should easily scale to accommodate growing datasets and user demands without compromising performance.
Comparison of Predictive Analytics Tools
Several predictive analytics tools are available in the market, each offering unique functionalities. The table below summarizes key features provided by some of the leading predictive analytics software solutions:
| Tool | Key Functionalities |
|---|---|
| Tableau | Data visualization, dashboard creation, and real-time analytics |
| IBM SPSS | Statistical analysis, predictive modeling, and data mining |
| Microsoft Azure ML | Machine learning model creation, automation of data preparation, and integration with Azure services |
| RapidMiner | Data preparation, machine learning, and predictive modeling with a user-friendly interface |
| SAS Advanced Analytics | Advanced statistical analysis, machine learning, and forecasting |
Importance of User Interface and User Experience
The user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) of predictive analytics software play a critical role in its adoption and effectiveness. A well-designed UI allows users to navigate through complex data sets easily, while good UX ensures that interactions with the software are intuitive and efficient. An intuitive design reduces the learning curve, enabling users with varying levels of technical expertise to leverage the software effectively.
Additionally, a responsive layout and visually appealing dashboards contribute to enhanced engagement, allowing users to focus on data insights rather than struggling with the software itself. In summary, the importance of UI and UX cannot be overstated; they significantly enhance user satisfaction and overall productivity when utilizing predictive analytics tools.
Types of Predictive Analytics Techniques
Predictive analytics is a powerful domain that encompasses various techniques designed to forecast outcomes based on historical data. Understanding the different types of predictive analytics techniques is crucial for professionals looking to leverage data for decision-making and strategic planning. Three primary techniques used in predictive analytics are regression, classification, and clustering. Each technique serves distinct purposes and is suited for different types of data and outcomes.
Below is a detailed overview of these techniques, including their applications and relevant scenarios.
Regression
Regression analysis is a statistical method used to understand the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. This technique is primarily used for predicting continuous outcomes.
- Application: Regression is commonly used in finance to predict stock prices based on various economic indicators.
- Scenario: A real estate company might use regression analysis to estimate property prices based on features such as location, size, and age of the property.
“Regression models help quantify the relationship between variables, assisting in precise forecasting.”
Classification
Classification involves categorizing data into predefined classes or groups. This technique is particularly useful when the outcome variable is categorical.
- Application: Classification is widely utilized in healthcare for diagnosing diseases based on patient data.
- Scenario: An online retailer might classify customers into segments (e.g., high-value, medium-value, low-value) based on their purchasing behavior to tailor marketing strategies.
“Classification techniques enable organizations to easily segment data for targeted analysis and actions.”
Clustering
Clustering is a technique used to group a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (or cluster) are more similar to each other than to those in other groups. It is particularly beneficial for exploratory data analysis.
- Application: Clustering is often used in customer segmentation to identify distinct groups within a customer base.
- Scenario: A marketing team may use clustering to find patterns in customer behavior, allowing them to develop personalized campaigns for different segments.
“Clustering helps in uncovering hidden patterns in data, providing insights that might not be visible through other analytical methods.”
Comparison Chart, Predictive Analytics Software
The following chart summarizes the differences and applications of regression, classification, and clustering techniques:
| Technique | Outcome Type | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Regression | Continuous | Stock price prediction, sales forecasting |
| Classification | Categorical | Fraud detection, customer segmentation |
| Clustering | Group Similarities | Market segmentation, social network analysis |
By understanding these foundational techniques, organizations can better utilize predictive analytics to drive decisions and strategies, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and competitive edge.
Implementation Strategies for Predictive Analytics
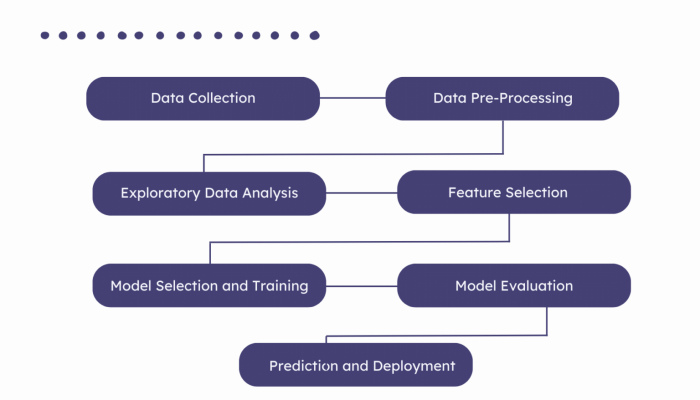
Implementing predictive analytics software in an organization involves a structured approach that ensures effective integration and operational success. The journey begins with understanding the organizational needs and ends with the continuous refinement of analytics processes. This section Artikels essential steps to facilitate a successful rollout of predictive analytics technologies.The implementation of predictive analytics software requires careful consideration of several steps, including defining objectives, engaging stakeholders, and ensuring that the right technological infrastructure is in place.
Successful adoption also hinges on the ability to analyze and clean the data effectively before it is utilized in predictive models, as the quality of predictions largely relies on the integrity of the data.
Steps for Implementing Predictive Analytics Software
To effectively implement predictive analytics software, the following steps should be taken:
1. Define Business Objectives
Clearly Artikel what the organization aims to achieve through predictive analytics, whether it’s improving customer retention, optimizing operations, or enhancing marketing efforts.
2. Engage Stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders from various departments to ensure that the analytics solutions meet diverse needs and gain buy-in across the organization.
3. Assess Data Infrastructure
Evaluate the existing data systems and software to determine whether they can support advanced analytics. This may involve investing in new technologies or enhancing current systems.
4. Data Collection and Preparation
Gather the necessary data from various sources and prepare it for analysis by cleaning, transforming, and integrating it.
5. Model Development
Choose appropriate predictive models and algorithms that align with business objectives, and train these models using the prepared dataset.
6. Testing and Validation
Rigorously test the models against real-world scenarios to validate their accuracy and effectiveness.
7. Deployment
Roll out the predictive analytics solutions and integrate them into the existing workflows of the organization.
8. Monitoring and Maintenance
Continuously monitor the performance of predictive models and make adjustments as needed to improve accuracy and relevance.
Best Practices for Data Preparation and Cleaning
Preparing and cleaning data is crucial for achieving reliable predictive analytics outcomes. Here are some best practices to follow:
Standardization
Ensure that data formats are consistent across different datasets, including date formats, currency, and categorical values.
Handling Missing Data
Develop a strategy for addressing missing data, whether through imputation, removal, or other techniques based on the nature of the data and the level of missingness.
Outlier Detection
Identify and address outliers that may skew results or affect model accuracy, using statistical methods or visualizations to pinpoint anomalies.
Data Transformation
Apply transformations to normalize data distributions where necessary, which can help in improving model performance.
Documentation
Maintain thorough documentation of data sources, cleaning processes, and transformation techniques to enhance reproducibility and transparency.
Common Challenges and Solutions During Implementation
The implementation of predictive analytics can present various challenges. Below is a list of common obstacles along with potential solutions to address them:
Data Quality Issues
Poor-quality data can lead to inaccurate predictions.
*Solution*
Invest time in thorough data cleaning and validation processes prior to analysis.
Resistance to Change
Employees may resist adopting new analytical tools and processes.
*Solution*
Provide training and create awareness about the benefits of predictive analytics to encourage acceptance.
Lack of Technical Expertise
An organization may lack the necessary data science skills to successfully implement predictive analytics.
*Solution*
Consider hiring or training staff in data science and analytics, or collaborate with external experts.
Integration Challenges
Difficulties in integrating analytics tools with existing systems can impede progress.
*Solution*
Ensure alignment between IT and analytics teams during the selection and implementation of tools to streamline integration.
Scalability Issues
As data volume grows, maintaining performance can become challenging.
*Solution*
Choose scalable analytics solutions that can grow with the organization’s data and analytical needs.
Case Studies of Predictive Analytics in Action
Predictive analytics has transformed various industries by enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on data-driven insights. Through the effective application of predictive analytics software, companies can anticipate trends, optimize operations, and enhance customer experiences. Here, we delve into several case studies that exemplify how predictive analytics has been successfully utilized across different sectors, showcasing measurable results and valuable lessons learned.
Retail: Target’s Customer Behavior Analysis
Target, a leading retail company, implemented predictive analytics to refine its marketing strategies and enhance customer engagement. By analyzing purchase history and shopping patterns, Target was able to predict customer preferences and identify buying signals. This enabled them to send personalized marketing offers that increased customer loyalty and sales.The measurable outcomes included:
- A 20% increase in sales from targeted promotions.
- Identification of customers who were likely to become mothers, allowing for tailored marketing campaigns.
The key lesson learned from this case was the importance of data integration and the ethical use of consumer data. Ensuring transparency in data usage helped build trust with customers.
Healthcare: Mount Sinai’s Patient Readmission Reduction
Mount Sinai Hospital utilized predictive analytics to address the issue of patient readmissions. By analyzing patient data, the hospital developed models to identify individuals at high risk of being readmitted within 30 days of discharge. This proactive approach allowed healthcare providers to implement targeted interventions.The measurable outcomes included:
- A 14% reduction in readmission rates across chronic care patients.
- Improved patient satisfaction scores due to tailored post-discharge follow-up.
The significant takeaway from this case was the potential of predictive analytics to enhance patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs through timely interventions.
Finance: American Express Fraud Detection
American Express adopted predictive analytics to enhance its fraud detection capabilities. By analyzing transaction patterns and customer behavior, the company created algorithms to flag potentially fraudulent activities in real-time, minimizing losses.The measurable outcomes included:
- A 30% decrease in fraud losses over two years.
- Increased confidence among customers, leading to higher transaction volumes.
The experience highlighted the necessity of continuous model refinement and the integration of machine learning techniques to stay ahead of evolving fraud tactics.
Manufacturing: General Electric’s Predictive Maintenance
General Electric (GE) implemented predictive analytics in its manufacturing processes to enhance equipment maintenance. By utilizing sensors and data analytics, GE predicted equipment failures before they occurred, optimizing maintenance schedules.The measurable outcomes included:
- A 10% reduction in maintenance costs.
- A 25% increase in equipment uptime, leading to improved production efficiency.
The key insight from this implementation was the value of real-time data collection and analysis, which enabled proactive maintenance strategies rather than reactive solutions.
Telecommunications: Verizon’s Customer Churn Prediction
Verizon leveraged predictive analytics to understand and mitigate customer churn rates. By analyzing customer usage patterns, billing history, and customer service interactions, Verizon identified at-risk customers and implemented retention strategies.The measurable outcomes included:
- A 15% reduction in customer churn within the first year of implementation.
- Enhanced customer engagement through personalized offers and improved services.
The primary lesson learned was that understanding customer behavior is essential for developing effective retention strategies, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive customer analytics framework.
Future Trends in Predictive Analytics
The landscape of predictive analytics is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in technology and an increasing demand for data-driven decision-making. As organizations seek to harness the power of their data, several trends are emerging that promise to reshape the capabilities and applications of predictive analytics software in the coming years. These trends not only highlight the direction of technological development but also emphasize the importance of integrating predictive analytics into business strategies.The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is significantly enhancing predictive analytics capabilities.
These technologies enable predictive models to learn from vast datasets, adapt to new information, and improve their accuracy over time. This evolution translates into more sophisticated analytics tools that can uncover deeper insights and provide actionable recommendations, making predictive analytics an indispensable part of business intelligence.
Emerging Trends in Predictive Analytics
Several key trends are shaping the future of predictive analytics tools, driving innovation and expanding their applicability across various industries. These trends reflect the growing sophistication and adoption of predictive analytics approaches.
- Increased Automation: Automation in data processing and model building is becoming prevalent. This reduces manual intervention, allowing analytics teams to focus on interpreting results and strategic planning.
- Real-Time Analytics: The demand for immediate insights is rising. Future predictive analytics tools will increasingly provide real-time data processing and analysis, enabling organizations to make decisions swiftly based on current data.
- Augmented Analytics: Leveraging AI and ML, augmented analytics will empower users to generate insights without requiring extensive technical skills, democratizing data analysis across various organizational levels.
- Explainable AI: As AI systems become more complex, there is a growing need for transparency in how predictions are made. Future analytics software will focus on providing understandable explanations for model outputs, enhancing trust and adoption.
- Integration with IoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) will feed vast amounts of data into predictive models, creating opportunities for advanced predictive analytics in sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and smart cities.
Potential Future Features and Enhancements
The evolution of predictive analytics tools will likely result in several innovative features and enhancements designed to meet the growing demands of users and the complexities of data management. The following table Artikels potential future enhancements that could redefine predictive analytics software.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Integration of NLP will allow users to interact with analytics tools using conversational language, making data analysis more intuitive. |
| Predictive Maintenance | Tools will evolve to predict equipment failures in real time, helping organizations minimize downtime and optimize maintenance schedules. |
| Personalized Recommendations | Advanced algorithms will deliver highly personalized insights and recommendations based on user behavior, enhancing customer experiences across platforms. |
| Collaborative Analytics | Features that allow teams to collaborate in real-time on data analysis will become standard, facilitating faster decision-making processes. |
| Enhanced Data Visualization | Predictive analytics tools will incorporate more dynamic and intuitive data visualization options, making complex data more accessible and understandable for users. |
These emerging trends and potential features are set to redefine how organizations leverage predictive analytics, fostering a culture of data-informed decision-making and driving competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Selecting the Right Predictive Analytics Software
Source: pathmonk.com
Choosing the right predictive analytics software is crucial for businesses looking to leverage data-driven insights. With various options available in the market, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of your specific business needs and the features that will best meet those requirements. The decision-making process involves evaluating software based on functionality, usability, integration capabilities, and vendor support.When considering predictive analytics software, it’s vital to establish criteria that align with your organization’s goals.
Factors such as scalability, ease of use, and the ability to integrate with existing systems should be on your checklist. Below are key criteria to consider when selecting the right predictive analytics software.
Criteria for Selecting Predictive Analytics Software
Identifying the right software starts with knowing what specific features your business needs. The following criteria can guide you in making an informed choice:
- Business Goals Alignment: Ensure the software aligns with your strategic objectives and can handle the specific types of analyses you require.
- User-Friendly Interface: The software should have an intuitive interface that allows users, regardless of technical skill level, to navigate easily.
- Data Handling Capabilities: Evaluate the software’s ability to process large datasets efficiently and its compatibility with various data formats.
- Analytical Techniques Offered: Look for software that provides a range of predictive techniques, such as regression analysis, machine learning, and time series forecasting.
- Integration Flexibility: The ability to seamlessly integrate with existing tools and systems is crucial for operational efficiency.
- Cost and Licensing: Consider the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance expenses.
Comparison of Popular Predictive Analytics Software
To make an informed selection, it can be helpful to compare some of the popular predictive analytics software options currently available. Below is a brief comparison highlighting key attributes:
| Software Name | Key Features | Target Users | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| IBM SPSS | Advanced statistical analysis, machine learning, and data mining. | Data scientists and statisticians. | Subscription-based pricing. |
| Microsoft Azure Machine Learning | Cloud-based platform, integration with Azure services, and automated ML. | Developers and data analysts. | Pay-as-you-go model. |
| SAS Enterprise Miner | Comprehensive data mining, model management, and scoring. | Large enterprises and analytics teams. | License-based pricing. |
| RapidMiner | Visual workflow, extensive data prep, and machine learning capabilities. | Business analysts and data scientists. | Freemium and subscription options. |
Importance of Vendor Support and Community Engagement
Vendor support and community engagement play significant roles in the effectiveness of predictive analytics software. Reliable vendor support ensures that you have access to assistance when troubleshooting or optimizing your software usage. Look for vendors that offer:
- Comprehensive Documentation: Detailed manuals and user guides can significantly reduce learning curves.
- Responsive Customer Service: Access to support channels such as chat, email, or phone can be invaluable during critical times.
- Active User Community: A vibrant community can provide additional resources, including forums for discussing challenges and sharing solutions.
- Regular Updates: Ensure the vendor commits to regular software updates for new features and security enhancements.
Choosing the right predictive analytics software involves careful consideration of features, vendor support, and alignment with business needs, ensuring a powerful tool for data-driven decision-making.
Ethical Considerations in Predictive Analytics

Source: devtalents.com
Predictive analytics has revolutionized decision-making across various sectors, but it also raises important ethical considerations. As organizations harness the power of data to forecast trends and behaviors, they must grapple with the potential ramifications of their analytics practices on individuals and society at large. The implications of using predictive models can significantly influence outcomes in areas such as hiring, law enforcement, and healthcare, necessitating a careful examination of ethical standards in their development and implementation.One of the primary ethical concerns in predictive analytics is the introduction of bias into models.
Bias can stem from various sources, including the data used for training algorithms and the design choices made by analysts. For instance, if a predictive model is trained predominantly on data from a specific demographic group, it may not perform well for others, leading to unfair treatment. Bias can manifest in numerous ways, such as reinforcing stereotypes, skewing risk assessments, or inadvertently discriminating against certain groups.
To mitigate these risks, organizations can adopt several best practices that promote fairness and accountability in predictive analytics.
Best Practices for Ethical Use of Predictive Analytics
Establishing ethical guidelines for predictive analytics requires proactive measures to ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability. Here are key practices that organizations should implement:
- Conduct Regular Bias Audits: Regularly evaluate models for bias by testing them against diverse datasets to identify any discrepancies in outcomes based on demographic factors.
- Ensure Data Diversity: Utilize diverse and representative datasets in model training to reduce the risk of biased predictions that may arise from homogeneous data sources.
- Promote Transparency: Clearly document the data sources, methodologies, and decision processes involved in developing predictive models to facilitate understanding and scrutiny.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve diverse stakeholders in the development process to gain various perspectives and minimize blind spots that could lead to ethical oversights.
- Implement Explainability Mechanisms: Develop models that not only provide predictions but also offer explanations for their decisions, helping users understand how outcomes are derived.
- Establish Accountability Structures: Create clear lines of accountability for analytics outcomes, ensuring that organizations are responsible for the impact of their predictive decisions.
- Adhere to Regulatory Guidelines: Stay informed about and comply with relevant laws and regulations governing data use and predictive analytics, such as data privacy laws and anti-discrimination regulations.
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can foster a more ethical environment for predictive analytics, ultimately improving trust and fairness in their decision-making processes. Implementing ethical considerations into predictive analytics not only protects individuals but also enhances the credibility and effectiveness of analytics initiatives across the board.
Conclusion
In summary, Predictive Analytics Software offers a powerful means to harness data for strategic advantage. As industries continue to embrace these advanced tools, the importance of ethical considerations, implementation strategies, and user-friendly interfaces cannot be overstated. By staying informed about the latest trends and techniques, businesses can leverage predictive analytics to unlock unprecedented opportunities for growth and innovation.
FAQ Insights
What is predictive analytics software?
Predictive analytics software uses statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze historical data and forecast future outcomes.
How can businesses benefit from predictive analytics?
Businesses can improve decision-making, enhance customer experiences, optimize operations, and reduce costs by leveraging predictive analytics.
What types of data are typically used in predictive analytics?
Data sources can include historical sales data, customer demographics, social media interactions, and operational metrics.
Are there any risks associated with predictive analytics?
Yes, risks include potential biases in data, privacy concerns, and the challenge of interpreting results accurately.
How can organizations ensure ethical use of predictive analytics?
Organizations can implement best practices such as regular audits, bias mitigation strategies, and transparency in data handling processes.